India's COVID-19 crisis reveals deep fractures in its health system
- Written by Kaaren Mathias, Lecturer in Health systems and policy, University of Canterbury
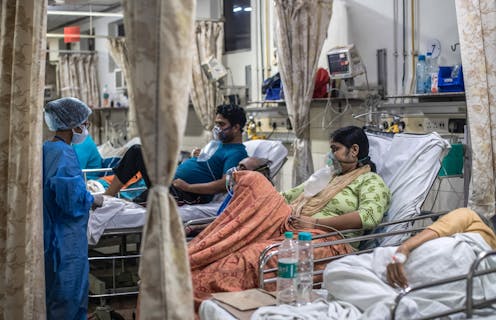
As India’s COVID-19 crisis continues, the percentage of the population testing positive for the virus has grown from 4.2% to 18.4% in the past 30 days.
With more than 300,000 new cases reported each day, hospitals and crematoria face collapse. Global media have been awash with heartbreaking images, statistics and stories showing the failure of the country’s health system in the face of surging infections and deaths.
The fracture lines in India’s health system have been developing for years. After decades of under-investment in healthcare and preventative health, India has one of the most privatised health systems in the world. As a consequence, healthcare costs are a leading cause of poverty.
As my recent research into rural mental health services shows, patients are caught between the under-resourced public sector and the profit-focused private health market. Some even many, have to “sell a buffalo to pay for a brain scan”.
Lack of investment in health
Back in 1946, India’s visionary Bhore Committee report declared in its preamble that:
No individual should fail to secure adequate medical care because of inability to pay for it.
In 2021, countries like Vietnam, South Korea and China have successfully contained COVID-19 with few deaths, while in India hundreds of thousands are sick with the virus without adequate medical care.
Promised oxygen generation plants have not been set up and most days I receive messages from colleagues in India seeking hospital beds and oxygen cylinders for loved ones gasping with severe COVID-19 infections.
The cost of healthcare pushes many into destitution. The global average of out-of-pocket healthcare costs is 18.2%, but in India the number is 62.7%.
While India has bounced along with 8% or higher growth in GDP for the past three decades, in 2018 the Indian government invested just 1.3% of GDP in healthcare. The average investment in health across South Asia is twice that at 3.5% and New Zealand and Australia spend over 9.0% of their GDP on health.
In the past two decades, use of public hospitals has dropped in India, from 43% in 1993-4 to 32%. In 2011, 70% of community health centres could not provide emergency obstetric care.
Not trustworthy and not trusted
My research into community health systems also underlines that in a country as diverse and vast as India, one size cannot fit all.
A key component of the treatment gap for people with neurological and mental health problems is that the system has not engaged with the priorities of local communities. The health system is not trustworthy and not trusted.
The consequences of India’s flawed health system are obvious. In the field of nutrition (the most basic building block of health) India is among the world’s top 20 for stunting (38.7% for children under five).
A third of children are not immunised and India’s ranking in basic health indicators compared to regional neighbours has dropped. In a list of 195 countries, ranked by the healthcare access and quality index, India is behind neighbours Bhutan and Sri Lanka.
The smaller but more resilient nations of Nepal and Bangladesh have a lower per capita GDP, but in 2020 both achieved an infant mortality rate of under 26 per 1000 live births. In India, more than 28 per 1000 babies died.
Read more: COVID in India: how the Modi government prioritised politics over public health
Rising infant and maternal deaths
India’s COVID-19 surge has revealed a system in disarray. During the country’s harsh lockdown in March and April last year, healthcare was less affordable, less accessible and of poorer quality.
While the private sector is much larger than the public sector, it handled less than 10% of cases during the first COVID-19 wave. Many private hospitals stayed closed for weeks.
Rationing of public services meant limits had to be introduced on the number of COVID-19 tests per day. Diverting resources (personnel, resources, hospital beds, policymaker attention) to respond to COVID-19 meant vaccination rates have slowed and maternal mortality worsened in the past 12 months.
As a consequence of disruptions to neonatal and child health services, India is expected to record an increase in the number of deaths among under fives by 15% (154,000 deaths) for 2020. The Indian economy is predicted to contract by 10% or more, which means more people in poverty and less cash to pay for health infrastructure and staff.
Read more: India COVID crisis: four reasons it will derail the world economy
Health systems are complex but they are not rigid. They can be resilient and responsive to new challenges like COVID-19. There are some simple steps India could take to strengthen its failing health system.
It could invest in the public sector — staff, infrastructure, medicines and equipment. It could set up accountable governance structures and prioritise care for those experiencing inequities in access and outcomes. Maybe COVID-19’s exposure of its fragmented health system will push India to rebuild, from the ground up.
Authors: Kaaren Mathias, Lecturer in Health systems and policy, University of Canterbury