what caused major climate change in the past?
- Written by James Renwick, Professor, Physical Geography (climate science), Te Herenga Waka — Victoria University of Wellington
Climate Explained is a collaboration between The Conversation, Stuff and the New Zealand Science Media Centre to answer your questions about climate change.
If you have a question you’d like an expert to answer, please send it to climate.change@stuff.co.nz
Earth had several periods of high carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere and high temperatures over the last several million years. Can you explain what caused these periods, given that there was no burning of fossil fuels or other sources of human created carbon dioxide release during those times?
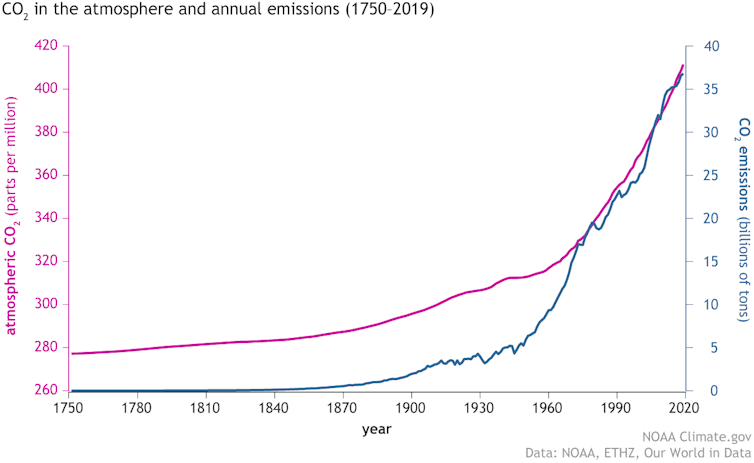
Burning fossil fuels or vegetation is one way to put carbon dioxide into the air – and it is something we have become very good at. Humans are generating nearly 40 billion tons of carbon dioxide every year, mostly by burning fossil fuels.
Carbon dioxide stays in the air for centuries to millennia and it builds up over time. Since we began the systematic use of coal and oil for fuel, around 300 years ago, the amount of carbon dioxide in the air has gone up by almost half.
 NOAA
Apart from the emissions we add, carbon dioxide concentrations in the air go up and down as part of the natural carbon cycle, driven by exchanges between the air, the oceans and the biosphere (life on earth), and ultimately by geological processes.
Natural changes in carbon dioxide
Every year, carbon dioxide concentrations rise and fall a little as plants grow in spring and summer and die off in the autumn and winter. The timing of this seasonal rise and fall is tied to northern hemisphere seasons, as most of the land surface on Earth is there.
The oceans also play an active role in the carbon cycle, contributing to variations over a few months to slow shifts over centuries. Ocean water takes up carbon dioxide directly in an exchange between the air and seawater. Tiny marine plants use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis and many microscopic marine organisms use carbon compounds to make shells. When these marine micro-organisms die and sink to the seafloor, they take the carbon with them.
Collectively, the biosphere (ecosystems on land and in soils) and the oceans are absorbing about half of all human-emitted carbon dioxide, and this slows the rate of climate change. But as the climate continues to change and the oceans warm up further, it is not clear whether the biosphere and oceans will continue absorbing such a large fraction of our emissions. As water warms, it is less able to absorb carbon dioxide, and as the climate changes, many ecosystems become stressed and are less able to photosynthesise carbon dioxide.
Earth’s deep climate history
On time scales of hundreds of thousands to millions of years, carbon dioxide concentrations in the air have varied hugely, and so has global climate.
This long-term carbon cycle involves the formation and decay of the Earth’s surface itself: tectonic plate activity, the build-up and weathering of mountain chains, prolonged volcanic activity, and the emergence of new seafloor at active mid-ocean faults.
Most of the carbon stored in the Earth’s crust is in the form of limestone, created from the carbon-based shells of marine organisms that sank to the ocean floor millions of year ago.
Carbon dioxide is added to the air when volcanoes erupt, and it is taken out of the air as rocks and mountain ranges weather and wear down. These processes typically take millions of years to add or subtract carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Read more:
Climate explained: how volcanoes influence climate and how their emissions compare to what we produce
In the present day, volcanoes add only a little carbon dioxide to the air, around 1% of what human activity is currently contributing. But there have been times in the past where volcanic activity has been vastly greater and has spewed large amounts of carbon dioxide into the air.
An example is around 250 million years ago, when prolonged volcanic activity raised atmospheric carbon dioxide levels dramatically. These were volcanic eruptions on a vast scale - lasting for around two million years and causing a mass extinction.
In the more recent geological past, the past 50 million years, carbon dioxide levels have been gradually dropping overall and the climate has been cooling, with some ups and downs. Once carbon dioxide concentrations became low enough (around 300 parts per million) between two and three million years ago, the current ice age cycle began, but the warming our emissions are causing is larger than the natural cooling trend.
Read more:
Climate explained: why we won't be heading into an ice age any time soon
While Earth’s climate has changed significantly in the past, it happened on geological time scales. The carbon in the oil and coal we burn represents carbon dioxide taken up by vegetation hundreds of millions of years ago and then deposited through geological processes over millennia. We have burned a significant proportion within a few centuries.
If human emissions of carbon dioxide continue to increase through this century, we could reach levels not seen for tens of millions of years, when Earth had a much warmer climate with much higher sea levels and no ice sheets.
NOAA
Apart from the emissions we add, carbon dioxide concentrations in the air go up and down as part of the natural carbon cycle, driven by exchanges between the air, the oceans and the biosphere (life on earth), and ultimately by geological processes.
Natural changes in carbon dioxide
Every year, carbon dioxide concentrations rise and fall a little as plants grow in spring and summer and die off in the autumn and winter. The timing of this seasonal rise and fall is tied to northern hemisphere seasons, as most of the land surface on Earth is there.
The oceans also play an active role in the carbon cycle, contributing to variations over a few months to slow shifts over centuries. Ocean water takes up carbon dioxide directly in an exchange between the air and seawater. Tiny marine plants use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis and many microscopic marine organisms use carbon compounds to make shells. When these marine micro-organisms die and sink to the seafloor, they take the carbon with them.
Collectively, the biosphere (ecosystems on land and in soils) and the oceans are absorbing about half of all human-emitted carbon dioxide, and this slows the rate of climate change. But as the climate continues to change and the oceans warm up further, it is not clear whether the biosphere and oceans will continue absorbing such a large fraction of our emissions. As water warms, it is less able to absorb carbon dioxide, and as the climate changes, many ecosystems become stressed and are less able to photosynthesise carbon dioxide.
Earth’s deep climate history
On time scales of hundreds of thousands to millions of years, carbon dioxide concentrations in the air have varied hugely, and so has global climate.
This long-term carbon cycle involves the formation and decay of the Earth’s surface itself: tectonic plate activity, the build-up and weathering of mountain chains, prolonged volcanic activity, and the emergence of new seafloor at active mid-ocean faults.
Most of the carbon stored in the Earth’s crust is in the form of limestone, created from the carbon-based shells of marine organisms that sank to the ocean floor millions of year ago.
Carbon dioxide is added to the air when volcanoes erupt, and it is taken out of the air as rocks and mountain ranges weather and wear down. These processes typically take millions of years to add or subtract carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Read more:
Climate explained: how volcanoes influence climate and how their emissions compare to what we produce
In the present day, volcanoes add only a little carbon dioxide to the air, around 1% of what human activity is currently contributing. But there have been times in the past where volcanic activity has been vastly greater and has spewed large amounts of carbon dioxide into the air.
An example is around 250 million years ago, when prolonged volcanic activity raised atmospheric carbon dioxide levels dramatically. These were volcanic eruptions on a vast scale - lasting for around two million years and causing a mass extinction.
In the more recent geological past, the past 50 million years, carbon dioxide levels have been gradually dropping overall and the climate has been cooling, with some ups and downs. Once carbon dioxide concentrations became low enough (around 300 parts per million) between two and three million years ago, the current ice age cycle began, but the warming our emissions are causing is larger than the natural cooling trend.
Read more:
Climate explained: why we won't be heading into an ice age any time soon
While Earth’s climate has changed significantly in the past, it happened on geological time scales. The carbon in the oil and coal we burn represents carbon dioxide taken up by vegetation hundreds of millions of years ago and then deposited through geological processes over millennia. We have burned a significant proportion within a few centuries.
If human emissions of carbon dioxide continue to increase through this century, we could reach levels not seen for tens of millions of years, when Earth had a much warmer climate with much higher sea levels and no ice sheets.
Authors: James Renwick, Professor, Physical Geography (climate science), Te Herenga Waka — Victoria University of Wellington
Read more https://theconversation.com/climate-explained-what-caused-major-climate-change-in-the-past-137874



















