Australians under 60 will no longer receive the AstraZeneca vaccine. So what's changed?
- Written by Paul Griffin, Associate Professor, Infectious Diseases and Microbiology, The University of Queensland
Australians aged under 60 will no longer receive first doses of the AstraZeneca vaccine due to the rare risk of a serious blood clotting disorder among people aged 50 to 59.
The government has accepted the advice of the Australian Technical Advisory Group on Immunisation (ATAGI), which recommends those aged under 60 now receive the Pfizer vaccine. It previously recommended Pfizer to those aged under 50.
The change is based on the advisory group’s assessment of the risks of the clotting disorder, called thrombosis and thrombocytopenia syndrome or TTS, versus benefits of the AstraZeneca vaccine in protecting against COVID-19.
While the risk of TTS is still very low overall, it is more common in younger age groups. And younger people are less likely to die or become seriously ill from COVID-19.
What is the clotting disorder and how common is it?
Thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS) is a rare clotting problem that can occur after vaccination with the AstraZeneca vaccine.
We don’t fully understand why TTS occurs, but we know it’s caused by an overactive immune response. This is a very different mechanism to clots people might get after travelling or being immobile for lengthy periods.
The condition involves blood clots as well as a depletion in blood clotting cells known as platelets. The clots associated with TTS can appear in parts of the body where we don’t normally see blood clots, like the brain or the abdomen.
In Australia we have now seen 60 cases of TTS, with 37 confirmed and 23 probable.
Of the 12 recent cases, seven occurred in people aged between 50 and 59.
Sadly, two people have died.
The risk of TTS reduces with age. For people aged under 50, there are 3.1 cases of TTS per 100,000 doses. This reduces to 1.9 cases for those aged 80 and above:
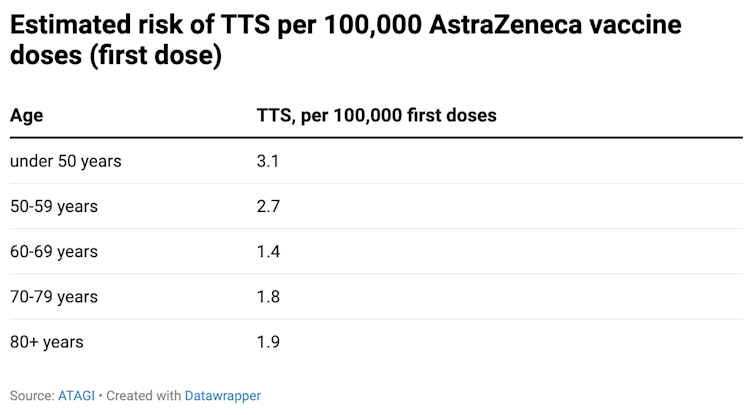 As awareness of TTS grows, clinicians’ ability to detect and diagnose the condition has also improved. This means the risk of becoming severely ill and dying from this condition has fallen dramatically.
How does this compare to the chance of dying from COVID-19?
Globally, 177 million cases of COVID-19 have been reported, with around 3.83 million deaths, or just over 2%.
The risk of dying from COVID-19 increases with age. The rates depend on the country you live in and your sex. In China, for instance, the death rate was reportedly:
for under-50s, less than 1%
50 to 59 years, 1.3%
60 to 69 years, 3.6%
70 to 79 years, 8%
80 and above, 14.8%.
In terms of data from Australia, in 2020, for every 600 people with COVID-19 aged in their 50s, one person died and 18 required admission to a hospital intensive care unit (ICU).
For every 600 people aged in their 70s with COVID-19, 24 died and 42 were admitted to ICU.
So the benefits of vaccination to prevent severe COVID-19 are greater among older age groups.
Read more:
A history of blood clots is not usually any reason to avoid the AstraZeneca vaccine
What if you’ve already had one dose?
If you’re aged 50 to 59 and have already had one dose, and didn’t have a significant reaction, the advice is for you to return for your second dose.
Relatively few Australians have received a second dose of the AstraZeneca vaccine. But data from the United Kingdom shows TTS appears much less commonly after second doses – 1.5 cases per million doses.
If you have concerns about the risk of TTS, talk to your doctor or vaccine provider.
In the future, as more evidence emerges and is assessed by Australia’s regulators, we may use other vaccines for follow-up doses. But this is not currently the recommendation.
Read more:
Can I get AstraZeneca now and Pfizer later? Why mixing and matching COVID vaccines could help solve many rollout problems
How does the advisory group decide?
ATAGI is a group of experts that closely monitors vaccines both in Australia and internationally for side effects, as well as how well they are working.
It also considers the amount of disease circulating that the vaccine is designed to protect from.
These factors are considered at the time of initial approval, and then monitored continuously. When some of these factors change, the way we use vaccines also needs to change.
Today’s change demonstrates the strength and robustness of the ongoing surveillance of adverse events of vaccines and our regulators’ commitment to ensure the safety of the community receiving these vaccines.
As awareness of TTS grows, clinicians’ ability to detect and diagnose the condition has also improved. This means the risk of becoming severely ill and dying from this condition has fallen dramatically.
How does this compare to the chance of dying from COVID-19?
Globally, 177 million cases of COVID-19 have been reported, with around 3.83 million deaths, or just over 2%.
The risk of dying from COVID-19 increases with age. The rates depend on the country you live in and your sex. In China, for instance, the death rate was reportedly:
for under-50s, less than 1%
50 to 59 years, 1.3%
60 to 69 years, 3.6%
70 to 79 years, 8%
80 and above, 14.8%.
In terms of data from Australia, in 2020, for every 600 people with COVID-19 aged in their 50s, one person died and 18 required admission to a hospital intensive care unit (ICU).
For every 600 people aged in their 70s with COVID-19, 24 died and 42 were admitted to ICU.
So the benefits of vaccination to prevent severe COVID-19 are greater among older age groups.
Read more:
A history of blood clots is not usually any reason to avoid the AstraZeneca vaccine
What if you’ve already had one dose?
If you’re aged 50 to 59 and have already had one dose, and didn’t have a significant reaction, the advice is for you to return for your second dose.
Relatively few Australians have received a second dose of the AstraZeneca vaccine. But data from the United Kingdom shows TTS appears much less commonly after second doses – 1.5 cases per million doses.
If you have concerns about the risk of TTS, talk to your doctor or vaccine provider.
In the future, as more evidence emerges and is assessed by Australia’s regulators, we may use other vaccines for follow-up doses. But this is not currently the recommendation.
Read more:
Can I get AstraZeneca now and Pfizer later? Why mixing and matching COVID vaccines could help solve many rollout problems
How does the advisory group decide?
ATAGI is a group of experts that closely monitors vaccines both in Australia and internationally for side effects, as well as how well they are working.
It also considers the amount of disease circulating that the vaccine is designed to protect from.
These factors are considered at the time of initial approval, and then monitored continuously. When some of these factors change, the way we use vaccines also needs to change.
Today’s change demonstrates the strength and robustness of the ongoing surveillance of adverse events of vaccines and our regulators’ commitment to ensure the safety of the community receiving these vaccines.
 ATAGI is continually reviewing the most up-to-date data on the safety and efficacy of our COVID vaccines.
James Ross/AAP
We’re fortunate to have excellent control of COVID-19 in Australia and low rates of severe disease. We’re also fortunate to have an alternate vaccine in the form of Pfizer, albeit still in relatively short supply.
Out of an abundance of caution and considering all of these and other factors, it makes sense to increase the age cut-off for the use of this vaccine in our country at present.
This may be subject to further changes in the future, in either direction, as the situation around us continues to evolve.
Read more:
How do we actually investigate rare COVID-19 vaccine side-effects?
ATAGI is continually reviewing the most up-to-date data on the safety and efficacy of our COVID vaccines.
James Ross/AAP
We’re fortunate to have excellent control of COVID-19 in Australia and low rates of severe disease. We’re also fortunate to have an alternate vaccine in the form of Pfizer, albeit still in relatively short supply.
Out of an abundance of caution and considering all of these and other factors, it makes sense to increase the age cut-off for the use of this vaccine in our country at present.
This may be subject to further changes in the future, in either direction, as the situation around us continues to evolve.
Read more:
How do we actually investigate rare COVID-19 vaccine side-effects?
Authors: Paul Griffin, Associate Professor, Infectious Diseases and Microbiology, The University of Queensland



















