In 100 years' time, maybe our food won't be grown in soil
- Written by Alex McBratney, Professor of Digital Agriculture & Soil Science; Director, Sydney Institute of Agriculture, University of Sydney
It takes a lot to make a room of soil scientists gasp.
Last month, I presented at the National Soils Conference in Canberra, and asked 400 colleagues a simple question: do you think soil will play as significant a role in food production in 100 years as it does today?
A sea of hands went up: the consensus was clearly “yes”. I demurred, saying I’m not so sure.
Gasps rippled across the room. Why say that? You’re a soil scientist! Are you crazy?
Read more: Eyes down: how setting our sights on soil could help save the climate
A century is a long time. Most of our scientific horizons seem no more than a decade or two away. But how we manage food and our environments needs very long-term, inspired thinking.
Within my concern about whether the future of food production is on terra firma, there is also a hope.
That hope rests in the desire that there will be adequate, quality food for all of the 10 billion, 15 billion or 20 billion people in the future. To achieve that, perhaps we don’t need to rely on the our planet’s thin skin of soil after all.
Future farming
We already see the advance of vertical and hydroponic farming, and the potential for growing meat-like protein in the lab. Synthetic biology is one way forward.
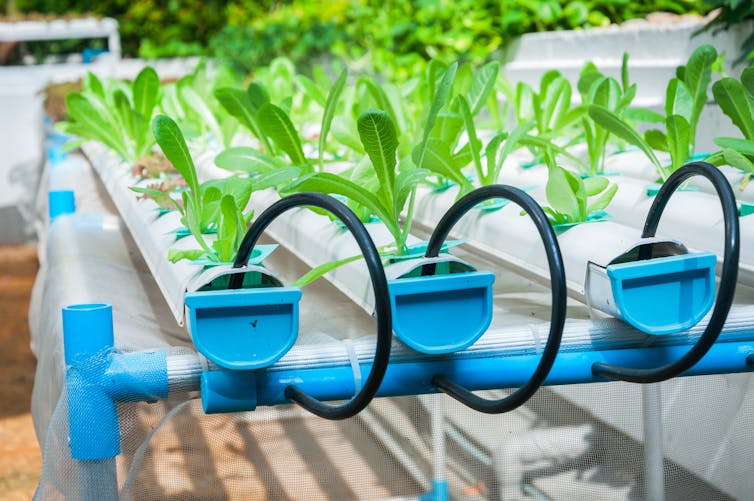 We have seen the advances of hydroponic farming.
www.shutterstock.com, CC BY
We have seen the advances of hydroponic farming.
www.shutterstock.com, CC BY
So will we have the technological know-how, and will we be able to afford the infrastructural investment to produce all our food away from natural soil within a century?
Technologically we would like to think this is possible. But will we have the need? Do we have the will?
There are two predominant modern movements in relation to food. The first is the ethical and environmental movement, which holds that food should be produced without harm to the environment or perhaps even to animals. Soil is an important – and non-renewable – part of the environment. This raises the crucial question of whether it can continue to sustain the world’s growing population.
Alongside this is the slow food movement, with its concern for the production of high-quality food of known provenance. It’s sometimes called “paddock to plate” or “field to fork”.
Already, modern food production techniques to manage energy and water use can potentially give 10 times the yield per unit area that normal field conditions provide. This could be transferred to vertical growing spaces, 100 units high.
Read more: Feeding cities in the 21st century: why urban-fringe farming is vital for food resilience
That alone means we would need just 0.1% of the land area we use now for food production. This could free up huge tracts of land to allow soil to recover from degradation, restoring ecosystems across the planet. It would represent a high-tech answer to the question of environmental ethics.
Returning areas of soil currently used for food production back to native vegetation could help us conserve wildlife, defend against floods, and provide natural buffer areas that can filter water and cycle nutrients. Locations may include soils in rainforests with copious biodiversity and voluminous water-cycling capability, or wetlands upstream of cities prone to flooding.
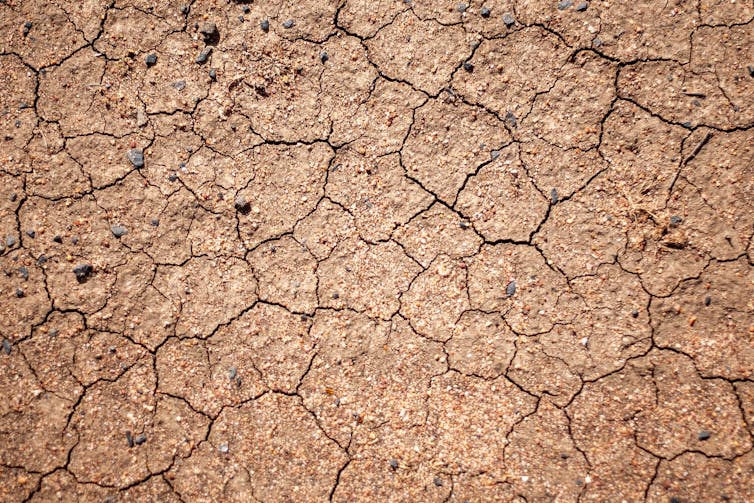 In Australia, the decline of carbon in cropping lands, soil erosion and nutrient imbalances continue largely unchecked and unabated.
www.shutterstock.com, CC BY
In Australia, the decline of carbon in cropping lands, soil erosion and nutrient imbalances continue largely unchecked and unabated.
www.shutterstock.com, CC BY
This approach is not necessarily incompatible with the slow food movement. Indeed, it could actually help the movement achieve its goals, because it would take the pressure off the world’s soils, thus ensuring there is enough high-quality soil left to pursue high-quality ethical production.
More food for more people
The United Nations Food & Agricultural Organisation predicts a need to double agricultural production by 2050 to meet the demand of an estimated population of 9.5 billion. This must be done while simultaneously maintaining functioning ecosystems; therefore securing soils and their life-supporting functions have never been more crucial.
In Australia, while soil care has improved, it is not yet sustainable. Widespread soil acidification and the decline of carbon in cropping lands, soil erosion and nutrient imbalances continue largely unchecked and unabated. With the new approach the appropriate soil and terroir could be dedicated to high-quality sustainable bespoke food and wine production.
The great loessial soils of North America, Russia and Ukraine are often regarded as the best in the world – they could be managed sustainably for the production of cereals for centuries to come. Even some of these most food-productive soils could be returned to their former pre-agricultural state. In Australia our famous red-brown earths might be more useful for forestry than being pressed into service for cereal production.
Read more: Climate change is making soils saltier, forcing many farmers to find new livelihoods
That said, the infrastructural costs of producing food entirely without soil will be enormous. It’s more likely we will land on a blended solution that combines highly engineered growing spaces and “under the sky” soil-based agriculture.
Over the coming century, our challenge will be to move away from our almost total reliance on soil – that mutable and vital thin skin of the earth – to allow large tracts of our most vulnerable soils to repair. Healing our wounded soils will be an important step on the road to global sustainability.
Authors: Alex McBratney, Professor of Digital Agriculture & Soil Science; Director, Sydney Institute of Agriculture, University of Sydney
Read more http://theconversation.com/in-100-years-time-maybe-our-food-wont-be-grown-in-soil-108049