our war with the environment is leading to pandemics
- Written by Fiona Armstrong, Executive Director, Climate and Health Alliance, Occasional Lecturer, School of Public Health and Human Biosciences, La Trobe University
The COVID-19 pandemic sweeping across the world is a crisis of our own making.
That’s the message from infectious disease and environmental health experts, and from those in planetary health – an emerging field connecting human health, civilisation and the natural systems on which they depend.
They might sound unrelated, but the COVID-19 crisis and the climate and biodiversity crises are deeply connected.
Each arises from our seeming unwillingness to respect the interdependence between ourselves, other animal species and the natural world more generally.
Read more: A major scorecard gives the health of Australia's environment less than 1 out of 10
To put this into perspective, the vast majority (three out of every four) of new infectious diseases in people come from animals – from wildlife and from the livestock we keep in ever-larger numbers.
To understand and effectively respond to COVID-19, and other novel infectious diseases we’ll likely encounter in the future, policymakers need to acknowledge and respond with “planetary consciousness”. This means taking a holistic view of public health that includes the health of the natural environment.
Risking animal-borne diseases
Biodiversity (all biological diversity from genes, to species, to ecosystems) is declining faster than at any time in human history.
We clear forests and remove habitat, bringing wild animals closer to human settlements. And we hunt and sell wildlife, often endangered, increasing the risk of disease transmission from animals to humans.
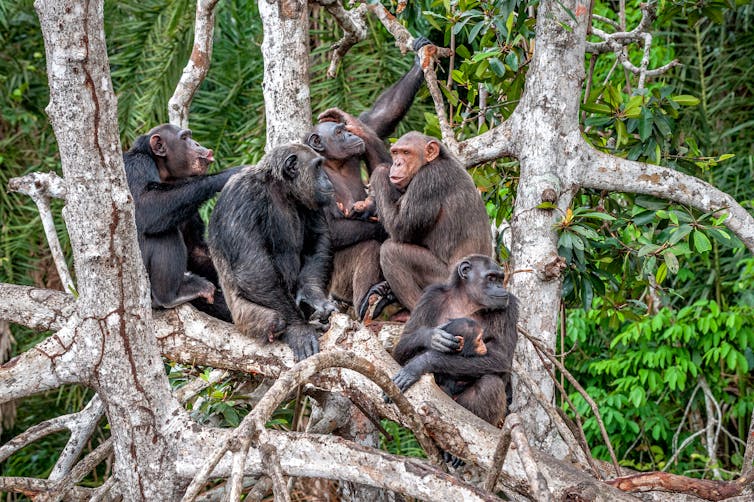 Land use changes forced chimpanzees and bats near human food resources.
Shutterstock
Land use changes forced chimpanzees and bats near human food resources.
Shutterstock
The list of diseases that have jumped from animals to humans (“zoonotic diseases”) includes HIV, Ebola, Zika, Hendra, SARS, MERS and bird flu.
Like its precursor SARS, COVID-19 is thought to have originated in bats and subsequently transmitted to humans via another animal host, possibly at a wet market trading live animals.
Ebola virus emerged in central Africa when land use changes and altered climatic conditions forced bats and chimpanzees together around concentrated areas of food resources. And Hendra virus is associated with urbanisation of fruit bats following habitat loss. Such changes are occurring worldwide.
What’s more, human-caused climate change is making this worse. Along with habitat loss, shifting climate zones are causing wildlife to migrate to new places, where they interact with other species they haven’t previously encountered. This increases the risk of new diseases emerging.
COVID-19 is just the latest new infectious disease arising from our collision with nature.
Read more: Here's what the coronavirus pandemic can teach us about tackling climate change
Due to its ability to spread at an alarming pace, as well as its relatively high mortality rate, it’s the sort of pandemic experts have been warning will arise from environmental degradation.
We saw this in 2018, for instance, when disease ecologist Dr Peter Daszak, a contributor to the World Health Organisation Register of Priority Diseases, coined the term “Disease X”. This described a then-unknown pathogen predicted to originate in animals and cause a “serious international epidemic”. COVID-19, says Daszak, is Disease X.
Climate change makes us vulnerable
But climate change is undermining human health globally in other profound ways. It’s a risk multiplier, exacerbating our vulnerability to a range of health threats.
Earlier this year, all eyes were on the extensive, life-threatening bushfires and the resulting blanket of smoke pollution. This exposed more than half of the Australian population to health harm for many weeks, and led to the deaths of more than 400 people.
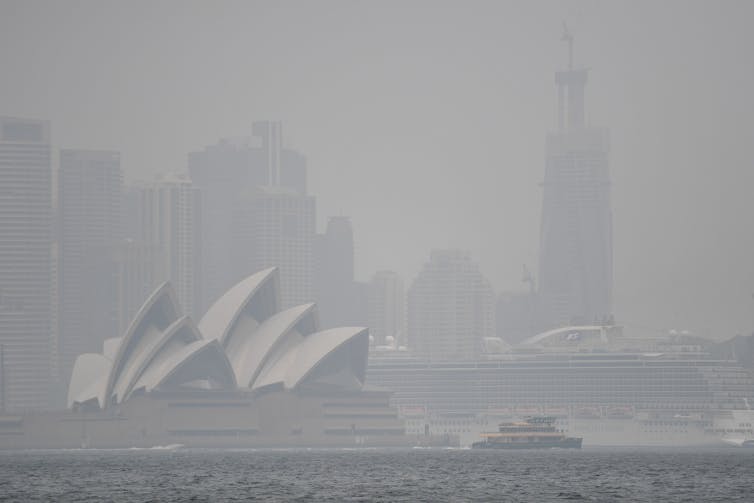 Bushfire smoke blanketed major cities in Australia and exacerbated respiratory illnesses.
AAP Image/Steven Saphore
Bushfire smoke blanketed major cities in Australia and exacerbated respiratory illnesses.
AAP Image/Steven Saphore
For infectious diseases such as COVID-19, air pollution creates another risk. This new virus causes a respiratory illness and, as with SARS, exposure to air pollution worsens our vulnerability.
Particles of air pollution also act as transport for pathogens, contributing to the spread of viruses and infectious disease across large distances.
A wake-up call
It might be clear to readers here that human health depends on healthy ecosystems. But this is rarely considered in policy decisions on projects that affect natural ecosystems – such as land clearing, major energy or transport infrastructure projects and industrial-scale farming.
Read more: The community-led movement creating hope in the time of coronavirus
The current COVID-19 pandemic is yet another warning shot of the consequences of ignoring these connections.
If we are to constrain the emergence of new infections and future pandemics, we simply must cease our exploitation and degradation of the natural world, and urgently cut our carbon emissions.
Controlling the pandemic appropriately focuses on mobilising human and financial resources to provide health care for patients and prevent human to human transmission.
But it’s important we also invest in tackling the underlying causes of the problem through biodiversity conservation and stabilising the climate. This will help avoid the transmission of diseases from animals to humans in the first place.
Read more: 222 scientists say cascading crises are the biggest threat to the well-being of future generations
The health, social and economic consequences of COVID-19 should act as a wake-up call for all governments to take stock, carefully consider the evidence, and ensure post COVID-19 responses reverse our war on nature. Because – as pioneering 20th century conservationist Rachel Carson argued – a war on nature is ultimately a war against ourselves.
Authors: Fiona Armstrong, Executive Director, Climate and Health Alliance, Occasional Lecturer, School of Public Health and Human Biosciences, La Trobe University