Thucydides and the plague of Athens
- Written by Chris Mackie, Professor of Classics, La Trobe University
The coronavirus is concentrating our minds on the fragility of human existence in the face of a deadly disease. Words like “epidemic” and “pandemic” (and “panic”!) have become part of our daily discourse.
These words are Greek in origin, and they point to the fact that the Greeks of antiquity thought a lot about disease, both in its purely medical sense, and as a metaphor for the broader conduct of human affairs. What the Greeks called the “plague” (loimos) features in some memorable passages in Greek literature.
One such description sits at the very beginning of western literature. Homer’s Iliad, (around 700BC), commences with a description of a plague that strikes the Greek army at Troy. Agamemnon, the leading prince of the Greek army, insults a local priest of Apollo called Chryses.
Apollo is the plague god – a destroyer and healer – and he punishes all the Greeks by sending a pestilence among them. Apollo is also the archer god, and he is depicted firing arrows into the Greek army with a terrible effect:
Apollo strode down along the pinnacles of Olympus angered
in his heart, carrying on his shoulders the bow and the hooded
quiver; and the shafts clashed on the shoulders of the god walking angrily. …
Terrible was the clash that rose from the bow of silver.
First he went after the mules and the circling hounds, then let go
a tearing arrow against the men themselves and struck them.
The corpse fires burned everywhere and did not stop burning.
Plague narratives
About 270 years after the Iliad, or thereabouts, plague is the centrepiece of two great classical Athenian works – Sophocles’ Oedipus the King, and Book 2 of Thucydides’ History of the Peloponnesian War.
Thucydides (c.460-400BC) and Sophocles (490-406BC) would have known one another in Athens, although it is hard to say much more than that for a lack of evidence. The two works mentioned above were produced at about the same time. The play Oedipus was probably produced about 429 BC, and the plague of Athens occurred in 430-426 BC.
Thucydides writes prose, not verse (as Homer and Sophocles do), and he worked in the comparatively new field of “history” (meaning “enquiry” or “research” in Greek). His focus was the Peloponnesian war fought between Athens and Sparta, and their respective allies, between 431 and 404 BC.
Thucydides’ description of the plague that struck Athens in 430 BC is one of the great passages of Greek literature. One of the remarkable things about it is how focused it is on the general social response to the pestilence, both those who died from it and those who survived.
 Statue portrait of historian Thucydides outside the Austrian parliament in Vienna.
Shutterstock
Statue portrait of historian Thucydides outside the Austrian parliament in Vienna.
Shutterstock
A health crisis
The description of the plague immediately follows on from Thucydides’ renowned account of Pericles’ Funeral Oration (it is important that Pericles died of the plague in 429 BC, whereas Thucydides caught it but survived).
Thucydides gives a general account of the early stages of the plague – its likely origins in north Africa, its spread in the wider regions of Athens, the struggles of the doctors to deal with it, and the high mortality rate of the doctors themselves.
Nothing seemed to ameliorate the crisis – not medical knowledge or other forms of learning, nor prayers or oracles. Indeed “in the end people were so overcome by their sufferings that they paid no further attention to such things”.
He describes the symptoms in some detail – the burning feeling of sufferers, stomachaches and vomiting, the desire to be totally naked without any linen resting on the body itself, the insomnia and the restlessness.
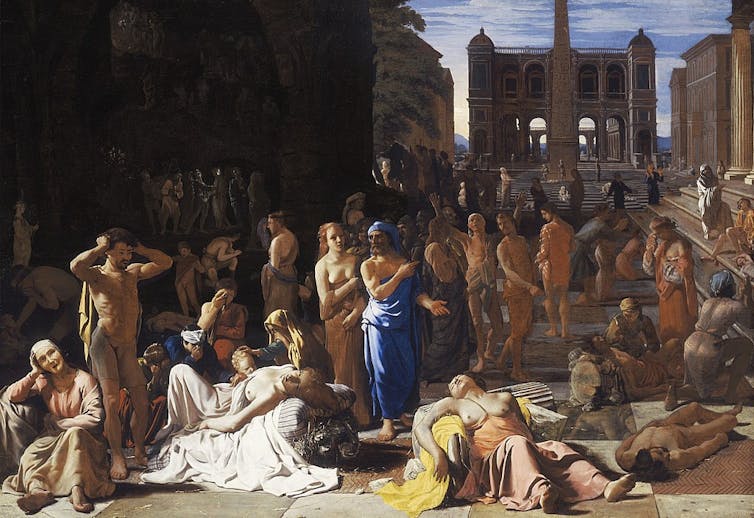 Michiel Sweerts’ Plague in an Ancient City (circa 1652).
Wikimedia
Michiel Sweerts’ Plague in an Ancient City (circa 1652).
Wikimedia
The next stage, after seven or eight days if people survived that long, saw the pestilence descend to the bowels and other parts of the body – genitals, fingers and toes. Some people even went blind.
Words indeed fail one when one tries to give a general picture of this disease; and as for the sufferings of individuals, they seemed almost beyond the capacity of human nature to endure.
Those with strong constitutions survived no better than the weak.
The most terrible thing was the despair into which people fell when they realized that they had caught the plague; for they would immediately adopt an attitude of utter hopelessness, and by giving in in this way, would lose their powers of resistance.
Lastly, Thucydides focuses on the breakdown in traditional values where self-indulgence replaced honour, where there existed no fear of god or man.
As for offences against human law, no one expected to live long enough to be brought to trial and punished: instead everyone felt that a far heavier sentence had been passed on him.
The whole description of the plague in Book 2 lasts only for about five pages, although it seems longer.
The first outbreak of plague lasted two years, whereupon it struck a second time, although with less virulence. When Thucydides picks up very briefly the thread of the plague a little bit later (3.87) he provides numbers of the deceased: 4,400 hoplites (citizen-soldiers), 300 cavalrymen and an unknown number of ordinary people.
Nothing did the Athenians so much harm as this, or so reduced their strength for war.
A modern lens
Modern scholars argue over the science of it all, not the least because Thucydides offers a generous amount of detail of the symptoms.
Epidemic typhus and smallpox are most favoured, but about 30 different diseases have been posited.
Thucydides offers us a narrative of a pestilence that is different in all kinds of ways from what we face.
The lessons that we learn from the coronavirus crisis will come from our own experiences of it, not from reading Thucydides. But these are not mutually exclusive. Thucydides offers us a description of a city-state in crisis that is as poignant and powerful now, as it was in 430BC.
Authors: Chris Mackie, Professor of Classics, La Trobe University
Read more https://theconversation.com/thucydides-and-the-plague-of-athens-what-it-can-teach-us-now-133155