Why is it so hard to stop COVID-19 misinformation spreading on social media?
- Written by Tobias R. Keller, Visiting Postdoc, Queensland University of Technology
Even before the coronavirus arrived to turn life upside down and trigger a global infodemic, social media platforms were under growing pressure to curb the spread of misinformation.
Last year, Facebook cofounder and chief executive Mark Zuckerberg called for new rules to address “harmful content, election integrity, privacy and data portability”.
Now, amid a rapidly evolving pandemic, when more people than ever are using social media for news and information, it is more crucial than ever that people can trust this content.
Digital platforms are now taking more steps to tackle misinformation about COVID-19 on their services. In a joint statement, Facebook, Google, LinkedIn, Microsoft, Reddit, Twitter, and YouTube have pledged to work together to combat misinformation.
Facebook has traditionally taken a less proactive approach to countering misinformation. A commitment to protecting free expression has led the platform to allow misinformation in political advertising.
More recently, however, Facebook’s spam filter inadvertently marked legitimate news information about COVID-19 as spam. While Facebook has since fixed the mistake, this incident demonstrated the limitations of automated moderation tools.
In a step in the right direction, Facebook is allowing national ministries of health and reliable organisations to advertise accurate information on COVID-19 free of charge. Twitter, which prohibits political advertising, is allowing links to the Australian Department of Health and World Health Organization websites.
 Twitter is directing users to trustworthy information.
Twitter.com
Twitter is directing users to trustworthy information.
Twitter.com
Twitter has also announced a suite of changes to its rules, including updates to how it defines harm so as to address content that goes against authoritative public health information, and an increase in its use of machine learning and automation technologies to detect and remove potentially abusive and manipulative content.
Previous attempts unsuccessful
Unfortunately, Twitter has been unsuccessful in its recent attempts to tackle misinformation (or, more accurately, disinformation – incorrect information posted deliberately with an intent to obfuscate).
The platform has begun to label doctored videos and photos as “manipulated media”. The crucial first test of this initiative was a widely circulated altered video of Democratic presidential candidate Joe Biden, in which part of a sentence was edited out to make it sound as if he was forecasting President Donald Trump’s re-election.
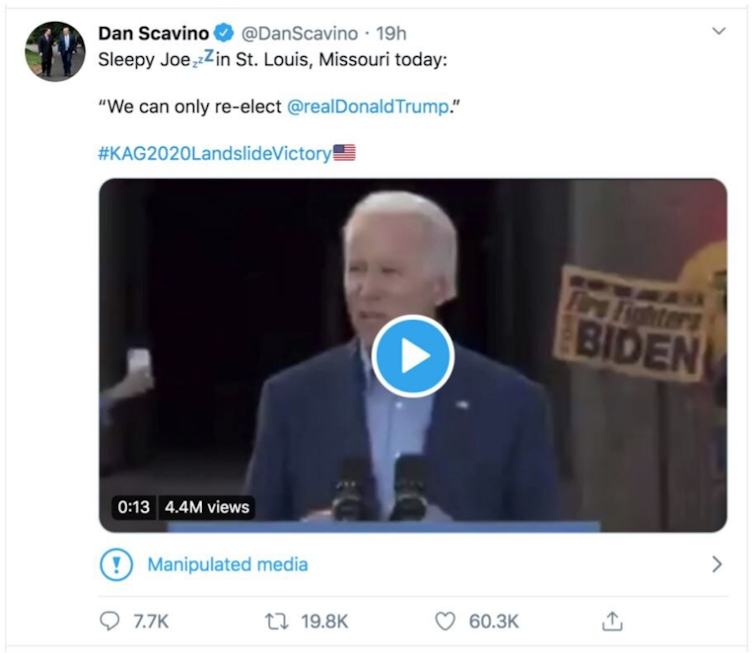 A screenshot of the tweet featuring the altered video of Joe Biden, with Twitter’s label.
Twitter
A screenshot of the tweet featuring the altered video of Joe Biden, with Twitter’s label.
Twitter
It took Twitter 18 hours to label the video, by which time it had already received 5 million views and 21,000 retweets.
The label appeared below the video (rather than in a more prominent place), and was only visible to the roughly 757,000 accounts who followed the video’s original poster, White House social media director Dan Scavino. Users who saw the content via reweets from the White House (21 million followers) or President Donald Trump (76 million followers), did not see the label.
Labelling misinformation doesn’t work
There are four key reasons why Twitter’s (and other platforms’) attempts to label misinformation were ineffective.
First, social media platforms tend to use automated algorithms for these tasks, because they scale well. But labelling manipulated tweets requires human labour; algorithms cannot decipher complex human interactions. Will social media platforms invest in human labour to solve this issue? The odds are long.
Second, tweets can be shared millions of times before being labelled. Even if removed, they can easily be edited and then reposted to avoid algorithmic detection.
Third, and more fundamentally, labels may even be counterproductive, serving only to pique the audience’s interest. Conversely, labels may actually amplify misinformation rather than curtailing it.
Finally, the creators of deceptive content can deny their content was an attempt to obfuscate, and claim unfair censorship, knowing that they will find a sympathetic audience within the hyper-partisan arena of social media.
So how can we beat misinformation?
The situation might seem impossible, but there are some practical strategies that the media, social media platforms, and the public can use.
First, unless the misinformation has already reached a wide audience, avoid drawing extra attention to it. Why give it more oxygen than it deserves?
Second, if misinformation has reached the point at which it requires debunking, be sure to stress the facts rather than simply fanning the flames. Refer to experts and trusted sources, and use the “truth sandwich”, in which you state the truth, and then the misinformation, and finally restate the truth again.
Third, social media platforms should be more willing to remove or restrict unreliable content. This might include disabling likes, shares and retweets for particular posts, and banning users who repeatedly misinform others.
For example, Twitter recently removed coronavirus misinformation posted by Rudy Guilani and Charlie Kirk; the Infowars app was removed from Google’s app store; and probably with the highest impact, Facebook, Twitter, and Google’s YouTube removed corona misinformation from Brasil’s president Jair Bolsonaro.
Finally, all of us, as social media users, have a crucial role to play in combating misinformation. Before sharing something, think carefully about where it came from. Verify the source and its evidence, double-check with independent other sources, and report suspicious content to the platform directly. Now, more than ever, we need information we can trust.
Authors: Tobias R. Keller, Visiting Postdoc, Queensland University of Technology