Why do more men die from coronavirus than women?
- Written by Jenny Graves, Distinguished Professor of Genetics, La Trobe University
All over the world – in China, Italy, the United States and Australia – many more men than women are dying from COVID-19.
Why? Is it genes, hormones, the immune system – or behaviour – that makes men more susceptible to the disease?
Read more: More testing will give us a better picture of the coronavirus spread and its slowdown
I see it as an interaction of all of these factors and it isn’t unique to the SARS-Cov-2 virus – the different response of men and women is typical of many diseases in many mammals.
The grim figures
In Italy and China deaths of men are more than double those of women. In New York city men constitute about 61% of patients who die. Australia is shaping up to have similar results, though here it’s mostly in the 70-79 and 80-89 age groups.
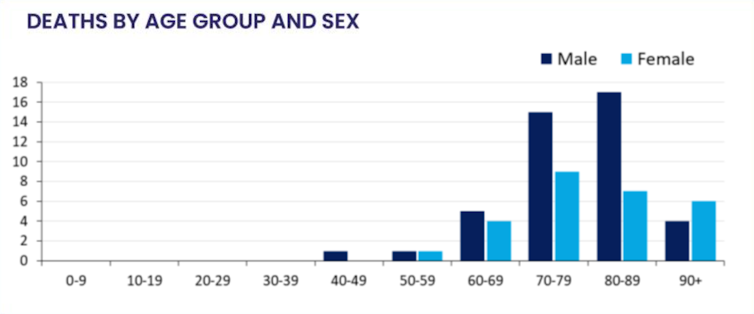 COVID-19 deaths in Australia (last updated April 19, 2020).
Australian Government, Department of Health
COVID-19 deaths in Australia (last updated April 19, 2020).
Australian Government, Department of Health
One major variable in severity of COVID-19 is age. But this can’t explain the sex bias seen globally because the increased male fatality rate is the same in each age group from 30 to 90+. Women also live on average six years longer than men, so there are more elderly women than men in the vulnerable population.
The other major factor is the presence of chronic diseases, particularly heart disease, diabetes and cancer. These are all more common in men than women, which might account for some of the bias.
But then we must ask why men are more vulnerable to the diseases that put them at greater risk of COVID-19.
Men and women are biologically different
Men and women differ in their sex chromosomes and the genes that lie on them. Women have two copies of a mid-sized chromosome (called the X). Men have only a single X chromosome and a small Y chromosome that contains few genes.
One of these Y genes (SRY) directs the embryo to become male by kick-starting the development of testes in an XY embryo. The testes make male hormones and the hormones make the baby develop as a boy.
In the absence of SRY an ovary forms and makes female hormones.
It’s the hormones that control most of the obvious visible differences between men and women – genitals and breasts, hair and body type – and have a large influence on behaviour.
The Y chromosome and hormones
The Y chromosome contains hardly any genes other than SRY but it is full of repetitive sequences (“junk DNA”).
Perhaps a “toxic Y” could lose its regulation during ageing. This might hasten ageing in men and render them more susceptible to the virus.
But a bigger problem for men is the male hormones unleashed by SRY action. Testosterone levels are implicated in many diseases, particularly heart disease, and may affect lifespan.
Men are also disadvantaged by their low levels of estrogen, which protects women from many diseases, including heart disease.
Male hormones also influence behaviour. Testosterone levels have been credited with major differences between men and women in risky behaviours such as smoking and drinking too much alcohol, as well as reluctance to heed health advice and to seek medical help.
The extreme differences in smoking rate between men and women in China (almost half the men smoke and only 2% of women) may help to account for their very high ratio of male deaths (more than double female). Not only is smoking a severe risk factor for any respiratory disease, but it also causes lung cancer, a further risk factor.
Smoking rates are lower and not as sex-biased in many other countries, so risky behaviour can’t by itself explain the sex difference in COVID-19 deaths. Maybe sex chromosomes have other effects.
Two X chromosomes are better than one
The X chromosome bears more than 1,000 genes with functions in all sorts of things including routine metabolism, blood clotting and brain development.
The presence of two X chromosomes in XX females provides a buffer if a gene on one X is mutated.
XY males lack this X chromosome backup. That’s why boys suffer from many sex-linked diseases such as haemophilia (poor blood clotting).
The number of X chromosomes also has big effects on many metabolic characters that are separable from sex hormone effects, as studies of mice reveal.
Females not only have a double dose of many X genes, but they may also have the benefit of two different versions of each gene.
This X effect goes far to explain why males die at a higher rate than females at every age from birth.
And another man problem is the immune system.
We’ve known for a long time that women have a stronger immune system than men. This is not all good, because it makes women more susceptible to autoimmune diseases such as lupus and multiple sclerosis.
But it gives women an advantage when it comes to susceptibility to viruses, as many studies in mice and humans show. This helps to explain why men are more susceptible to many viruses, including SARS and MERS.
There are at least 60 immune response genes on the X chromosome, and it seems that a higher dose and having two different versions of these gives women a broader spectrum of defences.
Sex differences in diseases – the big picture
Sex differences in the frequency, severity and treatment efficacy for many diseases were pointed out long ago. COVID-19 is part of a larger pattern in which males lose out – at every age.
This isn’t just humans – it is true of most mammals.
Are sex differences in disease susceptibility simply the by-catch of genetic and hormone differences? Or were they, like many other traits, selected differently in males and females because of differences in life strategy?
Read more: Dry, wet, barking, hacking: a guide to coughs in the time of coronavirus
It’s suggested that male mammals spread their genes by winning competitions for mates, hence hormone control of risky behaviour is a plus for men.
It’s also suggested female mammals are selected for traits that enhance their ability to care for young, hence their stronger immune system. This made sense for most mammals through the ages.
So the sex bias in COVID-19 deaths is part of a much larger picture – and a very much older picture – of sex differences in genes, chromosomes and hormones that lead to very different responses to all sorts of disease, including COVID-19.
Authors: Jenny Graves, Distinguished Professor of Genetics, La Trobe University
Read more https://theconversation.com/why-do-more-men-die-from-coronavirus-than-women-136038



















